KI-SIGS project iAuge: Homecare eye diagnostics and intelligent image analysis in ophthalmology
iAuge is a sub-project of the transregional joint project "KI-Space für intelligente Gesundheitssysteme” (KI-SIGS, engl. AI spaces for intelligent health systems). In cooperation with partners at the Universities of Lübeck, Kiel and Bremen, the University Medical Center Schleswig-Holstein (UKSH), Visotec GmbH and the UniTransferKlinik in Lübeck, new AI-based solutions for ophthalmic diagnostics will be developed. The main goal of the work at the Institute of Medical Informatics (IMI) is the development of optimized deep neural networks for the automatic AI-based evaluation of three-dimensional OCT images (OCT: optical coherence tomography) for the improved treatment of patients with eye diseases. The project is funded by the Federal Ministry of Economic Affairs and Energy for the period 2020-2023.
Within the subproject iAuge, an AI platform will be established to support the integrated treatment of patients with eye diseases such as the common age-related macular degeneration (AMD) and retinopathy centralis serosa (RCS). In addition to the AI support of multimodal image analysis for ophthalmologists, a deep-learning based automated data analysis for a novel homecare OCT application will be realized and incorporated into the KI-SIGS platform. This will enable the patient to monitor the disease at home, which is expected to lead to a significant improvement in therapy, especially for AMD patients. Continuous monitoring at home using homecare OCT images will automatically detect deterioration of the eye condition using an IMI developed AI system and determine individually optimal treatment time points.
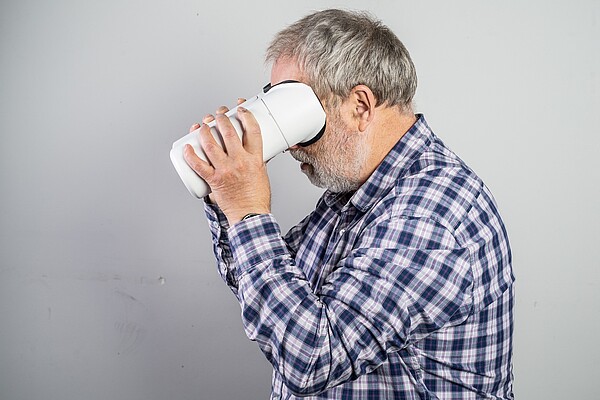
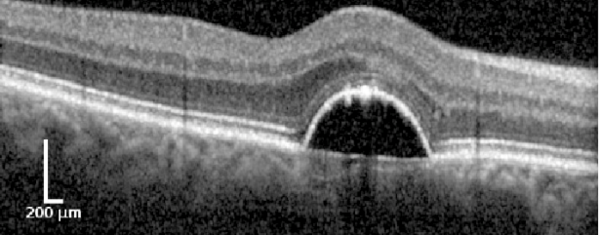
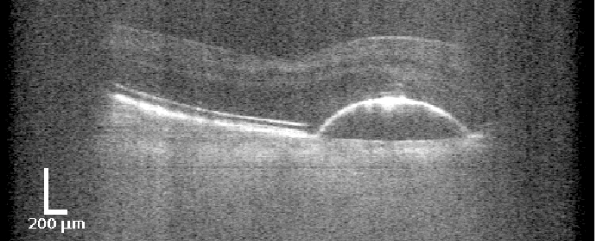
A technologically innovative, mobile OCT scanner is being developed by Visotec GmbH in cooperation with the Medizinisches Laserzentrum Lübeck GmbH for the homecare sector (Fig. 1). Together with the University Eye Clinic Kiel, this technology was validated on different patient cohorts and compared with already established, high-resolution OCT scanners. Visotec GmbH will provide image data of patients for the development of the algorithms and aims to commercialize the system. The large amount of daily acquired 3-dimensional image data requires new intelligent and efficient deep learning-based evaluation algorithms.For this purpose, the IMI designs and develops problem-optimized deep learning networks as well as image processing algorithms that quantitatively capture relevant AMD biomarkers (Fig. 2) in images of the home care OCT and quantify their temporal changes and relevance for therapy control. In addition, existing OCT images acquired in the clinic will be also incorporated into the development process. At the same time, reconstruction methods are being further developed at the Institute for Biomedical Optics (BMO) in order to compensate for motion and to improve the quality of relevant structures in the image. Due to its compact and cost-efficient design as well as its independent use by usually elderly patients with reduced visual acuity, the homecare application demands special requirements for the operation and evaluation of the data. An optimized user interface for the homecare OCT device is being developed in cooperation with Prof. Schöning (University of Bremen). Furthermore, in cooperation with the UniTransferKlinik Lübeck, the practical use of the system will be supported via a central AI platform and a demonstrator for the developed AI methods will be established.

Project Team
Cooperation Partners
Prof. Dr. Gereon Hüttmann
Institute for Biomedical Optics (BMO) of the University of Lübeck
Prof. Dr. Johann Roider, Dr. Claus von der Burchard
Department of Ophthalmology, UKSH Campus Kiel (UKSH Kiel)
Prof. Dr. Johannes Schöning
AG Human Computer Interaction, University Bremen (Uni Bremen)
Prof. Dr. Reinhard Koch, Monty Santarossa, University of Kiel
Multimedia Information Processing Group, University Kiel (Uni Kiel)
Prof. Dr. Martin Leucker, Dr. Tim Suthau
UniTransferKlinik, Lübeck (UTK)
Helge Sudkamp
Fa. Visotec GmbH, Lübeck

- Research
- AI und Deep Learning in Medicine
- Medical Image Processing and VR-Simulation
- Integration and Utilisation of Medical Data
- Sensor Data Analysis for Assistive Health Technologies
- Medical Image Computing and Artificial Intelligence
- Medical Data Science Lab
- Medical Deep Learning Lab
- Junior Research Group Diagnostics and Research of Movement Disorders
- Former Medical Data Engineering Lab
